One such metric is the profitability index (PI), otherwise known as the profit investment ratio or value investment ratio. PI involves calculating the viability and profitability of potential investments before investing in them, so that you can make informed decisions based on your evaluation. This article will provide a detailed guide for calculating PI, how to use it, and the difference between profitability index vs. NPV and other valuation metrics. In conclusion, the Profitability Index is a potent tool for investors and companies seeking to maximize their capital’s impact. The profitability index is used as an appraisal technique for potential capital outlays.
Formula for Calculating Profitability Index
It may not always indicate the correct decision when ranking projects but would certainly provide an insight into the cost-benefit efficiency of one monetary unit invested. Despite its relevance, this index uses just an estimate of the cost of capital in its calculation, so it should not be reviewed on a stand-alone basis. Combined with the Payback Period, Discounted Payback Period, and the Accounting Rate of Return, this ratio provides meaningful data to work with.
Real-World Examples of PI Calculation
For example, Garch Ltd could invest in Catcher even though the initial investment required is $600,000 while the company only has $550,000 available to invest. A positive NPV indicates that the investment will generate value, while a negative NPV suggests the investment may not meet the required rate of return on investment. To best understand how to calculate and rank investment projects using the profitability index equation, consider the following examples. In the energy sector, companies might use PI when deciding on infrastructure projects like building new power plants or expanding renewable energy sources.
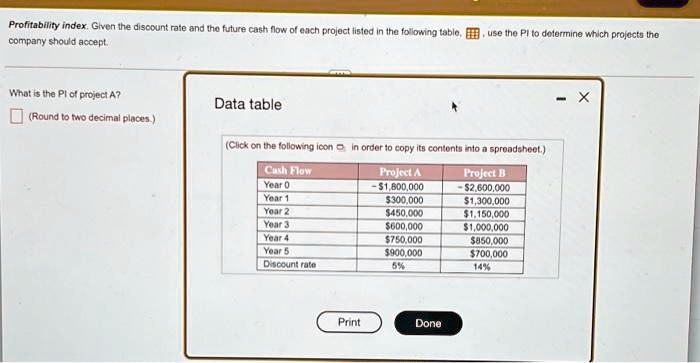
Step 1: Entering the Initial Cash Outlay
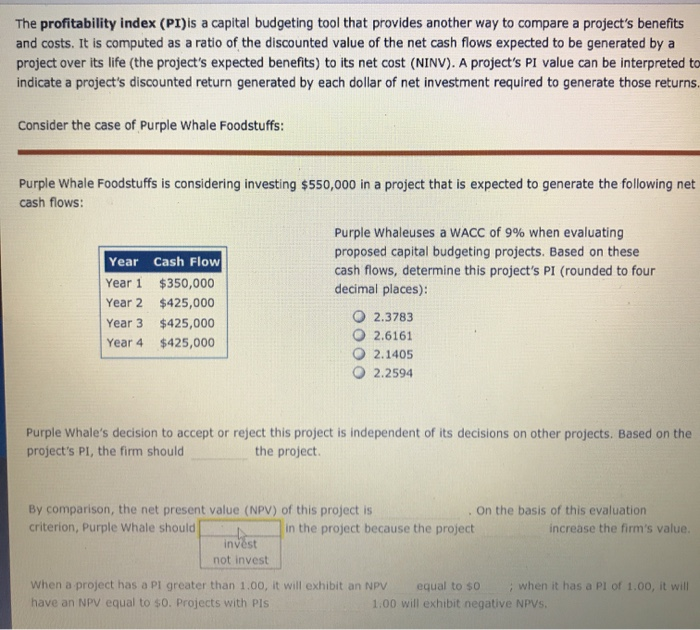
The present value of future cash flows is a method of discounting future cash to its current value, and requires the implementation of the time value of money calculation. This discounting occurs because the current value of $1 is not equivalent to the value of $1 received in the future. Money received closer to the present time is considered to have more value than money received further in the future.
- Discounted cash flows may unexpectedly differ in the future, which immediately makes us question the predictive accuracy of both PI and NPV figures as stand-alone metrics.
- Once the present value is determined, it is divided by the initial investment to find the PI.
- And lastly, investing in Catcher will earn Garch Ltd $155,000 in annual cash flow for the next 5 years.
- Mathematically, a value lower than one means the project’s present value (PV) is less than the initial investment.
- PI greater than 1 will be profitable and accepted and PI less than one will be rejected as it will create a loss.
It’s expressed as a numerical value that provides insight into an investment’s potential profitability. The new factory project is expected to cost $2 million and generate cash flows of $300,000 per year for the next 5 years, also with a discount rate of 10%. The profitability index is the ratio between the present value of future expected cash flows and the initial amount invested in the project. Given the following cash flows for a capital project, compute the NPV and IRR of the project.
Profitability Index Formula & Example
Given the substantial initial investments and long-term horizons of such projects, PI serves as a vital indicator of future profitability. It is the return where the PV of cash inflows gets equal to the cash outflows. It is the ratio that determines the relation between the present value of cash inflows and cash outflows.
It doesn’t matter the type of business that you operate or the industry that you are in. It also doesn’t matter if you’re a sole trader or a limited liability partnership. Generating profit and increasing that profit margin is the difference between keeping your doors open or closed. The best thing about this index is that it allows businesses to compare between different projects whenever they require choosing one out of the other. The projects having more chances of generating profits is the project that the firms are likely to choose.
Mathematically, a value lower than one means the project’s present value (PV) is less than the initial investment. A profitability index or ratio below 1 indicates that the project should be abandoned. It looks very much taxes and tax returns when someone dies frequently asked questions like the NPV equation except that the discount rate is the IRR instead of r, the required rate of return. A profitability index of 1 indicates breaking even, which is an indifferent result for potential investors.
You need to consider initial investment, the rate of return and future cash flows. The profitability index measures whether or not a project or investment will benefit your business. And this gets done by measuring the ratio between the initial capital investment and the present value of future cash flows. For example, a project with an initial investment of $1 million and a present value of future cash flows of $1.2 million would have a profitability index of 1.2. Based on the profitability index rule, the project would proceed, even though the initial capital expenditure required are not identified. The Profitability Index (PI) or profit investment ratio (PIR) is a widely used measure for evaluating viability and profitability of an investment project.
